Treatments
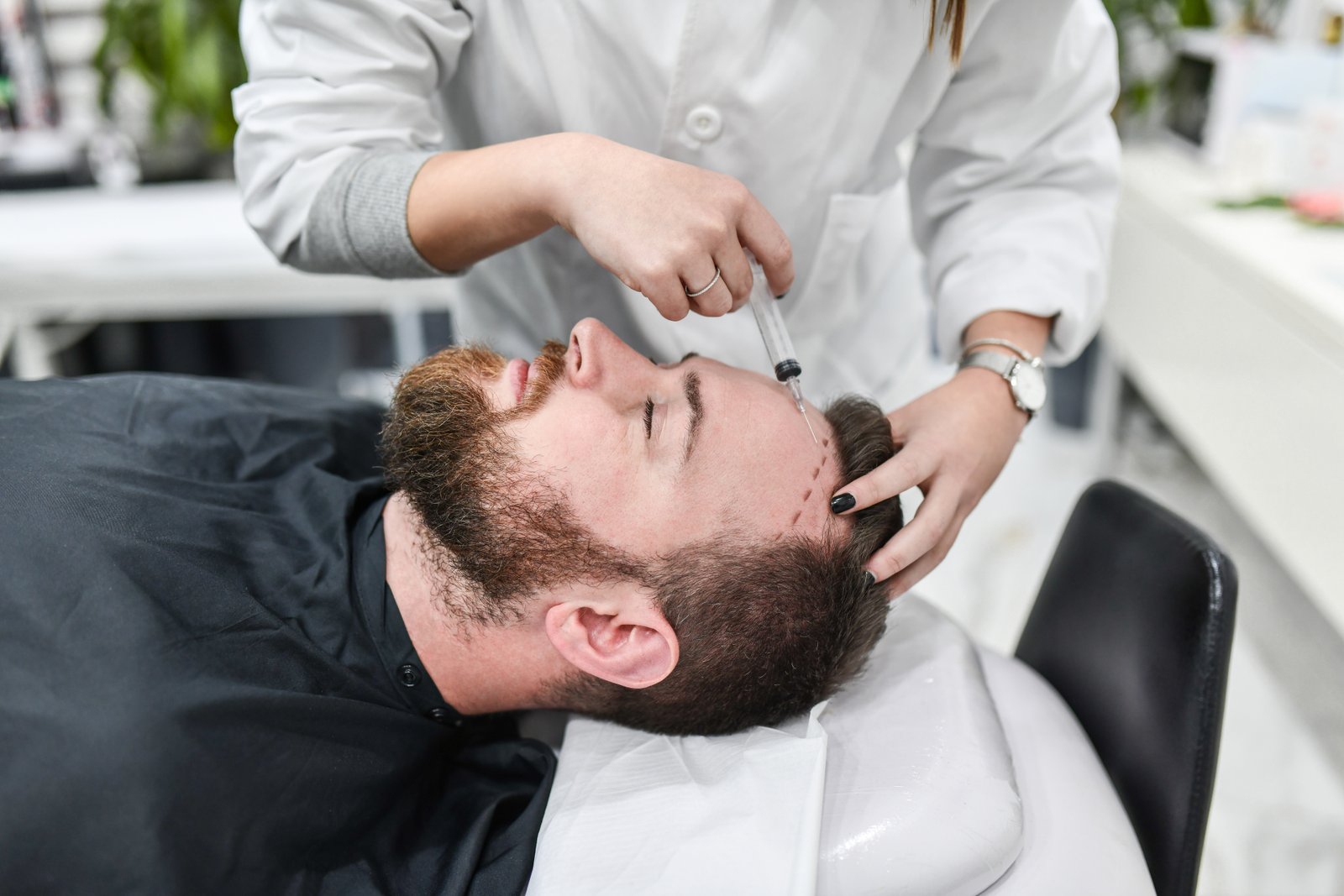
FUE Hair Transplant
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is a type of hair transplantation procedure. In FUE, individual hair follicles are extracted directly from the scalp and transplanted to the areas of the scalp where hair is thinning or balding. This method contrasts with Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), where a strip of scalp skin is removed, and hair follicles are harvested from the strip. The FUE procedure involves the following steps: 1. Preparation of the Donor Area: The surgeon shaves the area of the scalp where hair follicles will be extracted. 2. Extraction of Follicular Units: Using a specialized tool, the surgeon removes individual hair follicles from the scalp. This is usually done from the back of the head as this area is resistant to genetic hair loss. 3. Preparation of the Recipient Area: The surgeon prepares the area where the hair will be transplanted. This typically involves making small incisions or punctures in the scalp. 4. Transplantation: The extracted hair follicles are then implanted into the prepared incisions in the balding areas. 5. Recovery and Growth: After the procedure, the transplanted hair will fall out, which is normal. New hair growth from the transplanted follicles is usually seen within a few months. Advantages of FUE include: - Less Scarring: FUE leaves tiny dot scars scattered throughout the donor area, which are generally less noticeable than the linear scar left by FUT. - Reduced Recovery Time: As FUE is less invasive than FUT, the recovery time is typically shorter. - Flexibility in Hair Styles: The minimal scarring with FUE allows for shorter hairstyles that might expose scars from FUT. However, FUE is generally more time-consuming and often more expensive than FUT. It also requires a skilled surgeon to perform effectively. The suitability of FUE for a patient depends on various factors like the extent of hair loss, the quality and quantity of donor hair, and the patient's expectations.
 Türkçe
Türkçe Русский
Русский Кыргызча
Кыргызча Arabian
Arabian Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español